What you need to know about Salmonella
Since the beginning of 2022 a number of products have been recalled due to reports of food poisoning linked to an outbreak of Salmonella.
In 2020 it was disclosed that around 2.4 million cases of foodborne illnesses now occur every year in the UK - compared to approximately 1 million in 2009.
And so, with cases of food poisoning on the rise, it is crucial that the correct controls and measures are put in place to prevent outbreaks from occurring.
Serious stuff, but Erudus is on hand to tell you everything you need to know about salmonella, and how we can help you manage your microbiological data…
What is Salmonella?
Salmonella (salmonellosis) is a type of bacteria that causes food poisoning.
It is pathogenic (disease-causing) to humans, and if contracted affects the intestinal tract - triggering symptoms such as diarrhoea, stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting and a fever. Whilst these symptoms should only last around a week, the risk of becoming severely ill with food poisoning from salmonella is greater in young children, the elderly and people with low immune systems.
The presence of salmonella in food is typically due to inadequate cooking and through cross-contamination.
What products are Salmonella bacteria found in?
Salmonella bacteria are most commonly found in:
- Raw meat
- Undercooked poultry such as chicken or turkey
- Eggs
- Unpasteurised milk
However, the recent products recalled due to outbreaks of salmonella include dry foods such as chocolate, cakes and cookies, as well as pet food. Whilst not for human consumption, pet food does carry a potential risk for humans through direct handling, or indirectly through pet feeding bowls, utensils or contact with animal faeces.
Ready-to-eat foods are also at specific risk of causing food poisoning from salmonella, as no further processing is required.
How do I reduce the risk of salmonella?
Though raw meat may contain traces of salmonella, if cooked at the right temperature and for the correct length of time, the bacteria present will be killed - making it safe to eat.
Most forms of food poisoning can be avoided by following advice on the 4Cs of food hygiene:
- Chilling
- Cleaning
- Cooking
- (Avoiding) Cross-contamination
Do I need to test for salmonella?
The presence of salmonella - specifically in ready-to-eat food - is considered to be a health hazard regardless of the level of contamination.
Therefore it is essential that microbiological testing is being conducted regularly, with the methods, frequency and specified limits documented. (See more information at the BRCGS website).
The food safety criteria for the presence of salmonella varies depending on the specific food type. For example, for “pre-cut fruit and vegetables (ready-to-eat)”, 5 samples should be taken from processing areas and equipment used in food production, with the result being an absence in 25g to be a low risk.
More information regarding the specific safety criteria for different food products can be found here.
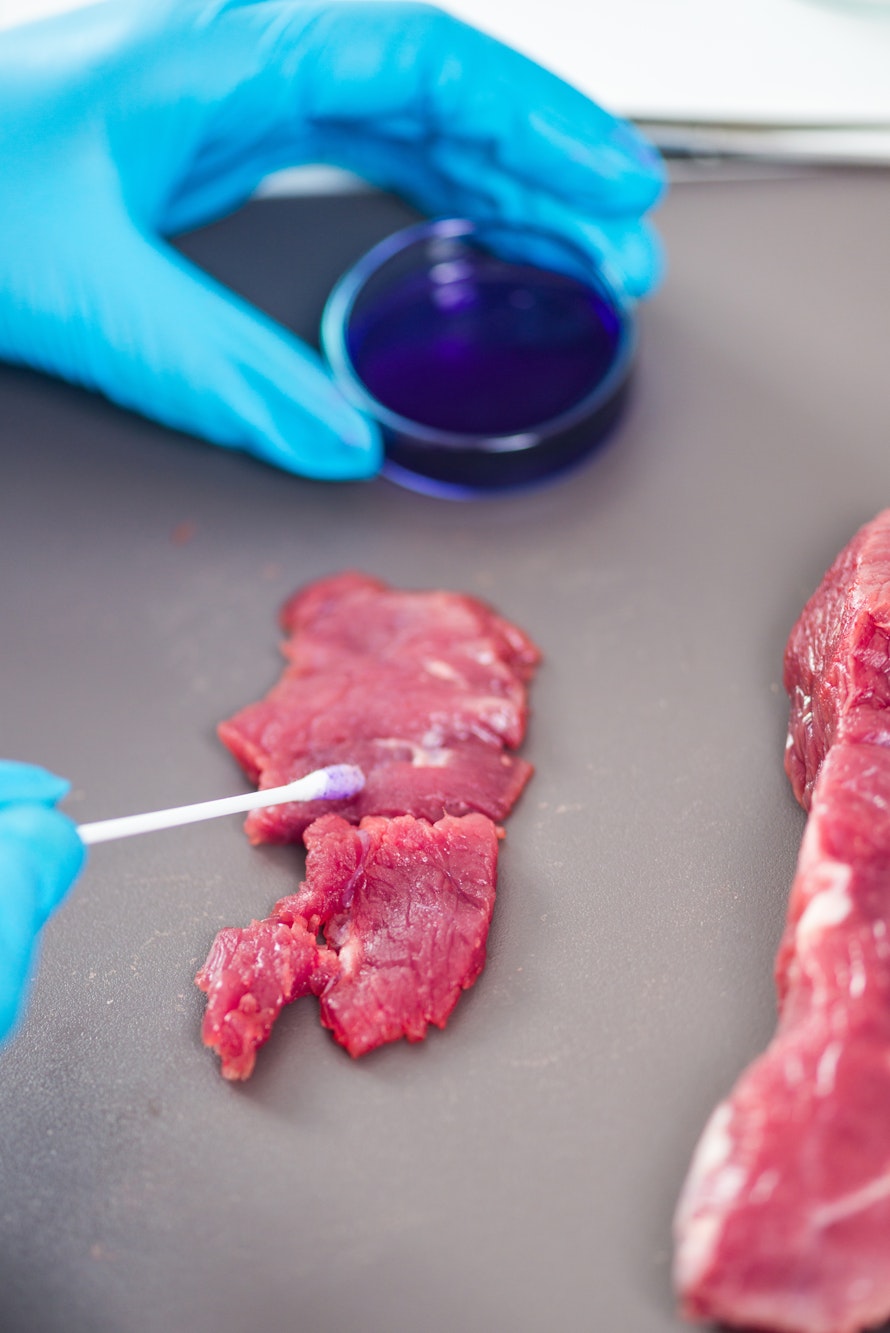
If the presence of salmonella is detected, an immediate investigation of the food origin, production process and environment should be conducted, investigative food samples should be taken, and environmental monitoring should be put into consideration.
Guidelines for Assessing the Microbiological Safety of Ready-to-Eat Foods Placed on the Market can be found here.
It is crucial that businesses have a plan and system in place to effectively manage a potential outbreak of salmonella, including the possibility of withdrawal and recall of products should it be required.
How can Erudus help?
You may also be interested in…


You may also be interested in…
The importance of using Microbiological fields
ReadProduct specifications should include specific limits for all microbiological data, including salmonella. Why? Because these limits are essential to ensure that it’s clear when a product is out of specification for testing conducted - meaning the appropriate action can be taken.
Erudus allows you to fill in Microbiological Fields for your products so that you can make this information easily and readily available to anyone who needs it - for example Wholesalers and Caterers.
It is important that all microbiological data is up to date and accurate on specifications, as this information is often used by Wholesalers and healthcare professionals to clearly display the quality and food safety standards expected.
For more information on the microbiological fields present in Erudus please see our guide to the importance of microbiological fields.
Further Resources
You may also be interested in…


You may also be interested in…
Erudus… Showcases BRCGS Certification
ReadYou may also be interested in…


You may also be interested in…


