The importance of using Microbiological fields

With listeria hitting the news for being the reason behind several food product recalls it’s never been more important for suppliers to understand microbiological criteria and prove they are compliant. Erudus allows you to fill in microbiological fields for your products so that you can make this information available to those who need to see it. And because we want to make it as easy as possible to share this crucial data, we’ve put together a handy guide to microbiological fields and standards…
What is Microbiological criteria and why is it important?
Put simply, microbiological hazards in food are a major source of food-borne diseases. Microbiological criteria give guidance on the acceptability of food and their manufacturing, handling and distribution processes. The use of microbiological criteria should form an integral part of the implementation of HACCP-based procedures and other hygiene control measures. (Find out more on that subject here).
As bacteria cannot be seen by the naked eye, testing needs to be completed to ensure foods are monitored to be safe for consumption. Specifically, when foods are ready-to-eat special care needs to be taken to ensure food safety, by verifying the absence of microorganisms such as Salmonella, E.coli, Listeria and Clostridium botulinum.
Pathogenic bacteria (such as Salmonella, Campylobacter, Listeria) contribute to a significant amount of food-borne illness. Testing against specific microbiological criteria standards provides a way of measuring the processes to ensure that potential contamination is avoided and controlled. The results of testing can also help to validate whether a Manufacturer’s HACCP procedures are meeting the food safety standards required.
What are Microbiological fields on Erudus?
Erudus allows Manufacturers to add information about microbiological testing and standards to product specifications, as seen below.
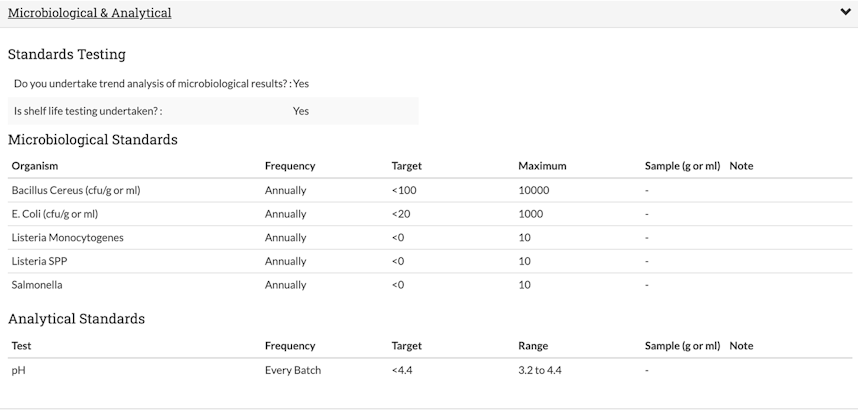
Why all Manufacturers should be sharing Microbiological Data on Erudus
It’s important that microbiological data fields held on Erudus are completed and kept up to date, because during an external audit, it is likely that the auditor will want to see what microbiological sampling plan there is in place, and the standards you are working towards.
Both STS and BRCGS have specific standards around microbiological criteria, for which suppliers may be required to demonstrate their compliance against product specifications, e.g. by providing evidence of their microbiological test results.
To ensure compliance, it is important that the microbiological fields are being used efficiently on Erudus as a way to document the relevant microbiological standards. This also ensures that our users have the most accurate information in regards to the microbiological data relevant to the product.
Following this, if a product supplied to a healthcare professional and/or Wholesaler is out of specification, corrective action would need to be taken. You can learn more about that here.
And in general, microbiological data on food specifications are often used by Wholesalers and healthcare professionals to clearly display the quality and food safety standards expected. Therefore, new and existing products need to be monitored and updated regularly (if required) to ensure standards are being met.
Reference to the Importance of Microbiological Standards within BRCGS and STS:
- Specifications for raw materials and primary packaging shall be adequate and accurate and ensure compliance with relevant safety and legislative requirements. The specifications shall include defined limits for relevant attributes of the material which may affect the quality or safety of the final products (e.g. chemical, microbiological or physical standards) (3.6.1 - BRCGS Issue 8)
- There shall be a scheduled programme of product testing which may include microbiological, chemical, physical and organoleptic testing according to risk. The methods, frequency and specified limits shall be documented (5.6.1.1 - BRCGS Issue 8)
- The Company shall establish and maintain product and ingredient specifications to include, “physical” properties, microbiological standards, food standards, quality and composition standards, packaging and labelling where appropriate, having regard to any legislative requirements and good manufacturing practice (8.4.3 - STS Food Safety Standard: For food suppliers & distributors)
- In respect of ready to eat foods supplied for use by vulnerable groups, supplier approval procedures must consider the ingredient supplier’s Listeria monocytogenes risk management and controls (8.11.1 - STS Food Safety Standard: For food suppliers & distributors)
A Guide to Different Bacteria
Let’s take a look into a few of the specific microbiological fields on Erudus, showing the relevance and importance of including data standards within your specifications:
Listeria:
Listeriosis is a rare infection caused by bacteria called listeria, that is usually caused by eating food containing listeria bacteria. Listeria is mainly an issue with high risk foods, including:
- Cooked sliced meats
- Cured meats
- Smoked fish
- Cooked shellfish
- Blue veined and mould-ripened soft cheeses
- Pate
- Pre-packaged sandwiches and salads
Foodborne illness as a result of consuming Listeria is rare compared to many others, however if infected it can cause serious symptoms and even death in certain vulnerable groups. STS are most notably known for providing accreditation to manufacturers supplying food to the NHS. Because of this, the “STS Food Safety Standard: For food suppliers & distributors” is clear on how vital the incorporation of testing for Listeria is within high risk foods.
Salmonella:
Salmonella infection (salmonellosis) is a common bacterial disease that affects the intestinal tract. Salmonella bacteria are most often found in:
- Raw meat
- Undercooked poultry such as chicken or turkey
- Eggs
- Unpasteurised milk
Cross-contamination of ready-to-eat foods that are not going to be cooked or are undercooked can also lead to incidents of salmonella food poisoning. The presence of Salmonella species in ready-to-eat food, no matter the level, is considered to be a risk to a persons health.
Campylobacter:
Campylobacter is caused by eating or drinking products contaminated by the Campylobacter species.
C. jejuni and C. coli are the 2 types of Campylobacter that most commonly cause illness. Foods Campylobacter is most commonly found in include:
- Raw or undercooked meat, especially poultry
- Unpasteurised milk
- Untreated water
Although it does not normally grow in food, it spreads easily, therefore there is a greater risk of cross-contamination of ready to eat foods during preparation.
Campylobacter is the most common cause of food poisoning in the UK. Consuming a very small amount is sufficient to cause infection. Therefore, especially as you can’t see, smell or taste it on food, it is crucial that testing is conducted on products to reduce the risk of infection. Find out more here.





