14 Allergens: The Different Types of Tree Nut
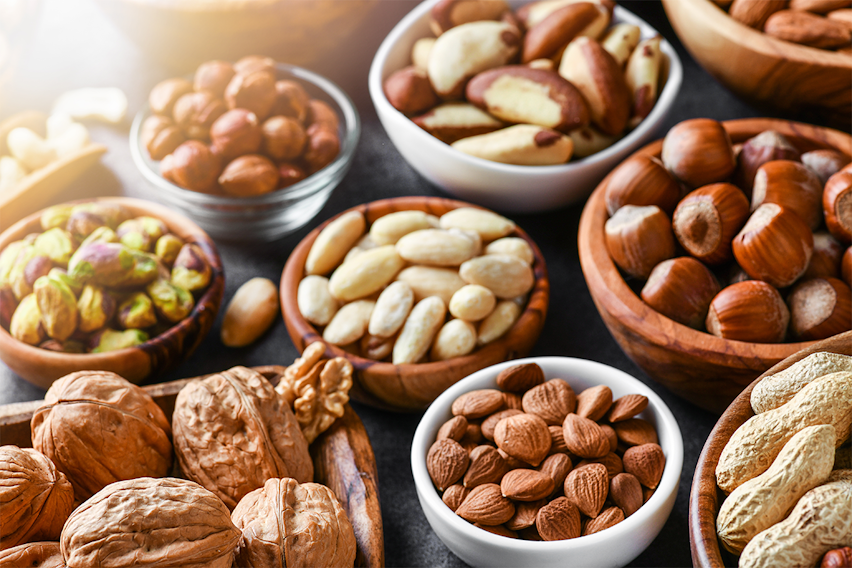

Tree Nuts are one of the 14 major food allergens, and as a major ingredient in many of the world’s cuisines, one of the ones consumers are most likely to come across. But unlike most of the other allergens (Cereals containing Gluten being an exception) there are several different varieties of Tree Nut, which are used in different types of food and which can trigger different reactions in different people.
We already took a deep dive into the symptoms of a Tree Nut allergy and the foods to avoid, but now we’re taking an even closer look at the different varieties of Tree Nuts, the dishes you might find them in, and the likelihood of being allergic to more than one type.
We’ve decided to focus on the Tree Nut subcategories found on Erudus. These are:
- Almond nuts
- Brazil nuts
- Cashew nuts
- Hazelnuts
- Macadamia nuts
- Pecan nuts
- Pistachio nuts
- Queensland nuts
- Walnuts
Now let’s find out more about them...
What are Tree Nuts?
Put simply, "Tree Nuts" are nuts (or seeds, to be botanically correct) that grow on fruit-bearing trees.
Almond nuts
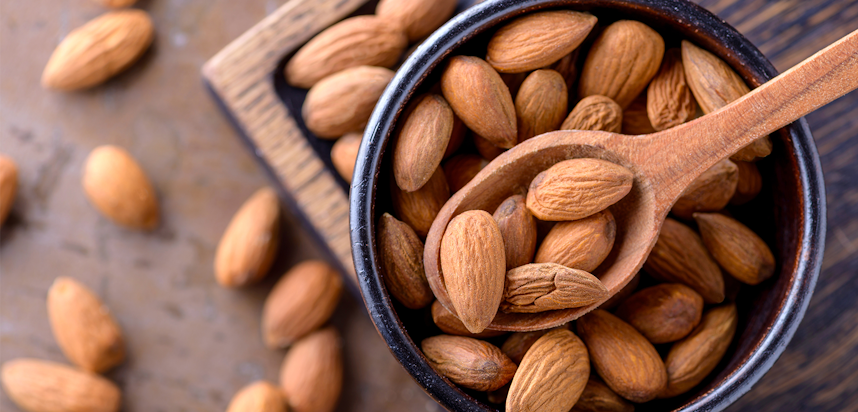

What are Almond Nuts?
Though commonly known as “nuts”, Almonds are the cultivated seed of the Almond tree, a species native to Iran and the countries surrounding it. Almonds belong to the Rosaceae family, and are well known for their health benefits.
Almonds are particularly rich in protein, fibre, calcium, riboflavin and niacin. They also contain a high amount of Vitamin E, and unsaturated fat (which helps manage cholesterol) and are though to improve lipid, or fat, levels in the blood, which can benefit the heart.
Their reputation for aiding weight management is a result of their protein content combined with unsaturated fat - they allow people to feel fuller for longer and regulate blood sugar.
Almonds can be found in
Breakfast cereals, snack bars, Bakewell tart, curry, Frangipane, Simnel cake, Macarons, and very frequently are eaten alone (either salted, sugared or plain) as a snack.

Almonds are also a major ingredient in marzipan, which is used for cakes, biscuits, sweets.
Potential cross-reactivity with
To a small extent Cashews and Pistachios and to a very small extent Walnuts.
Brazil nuts
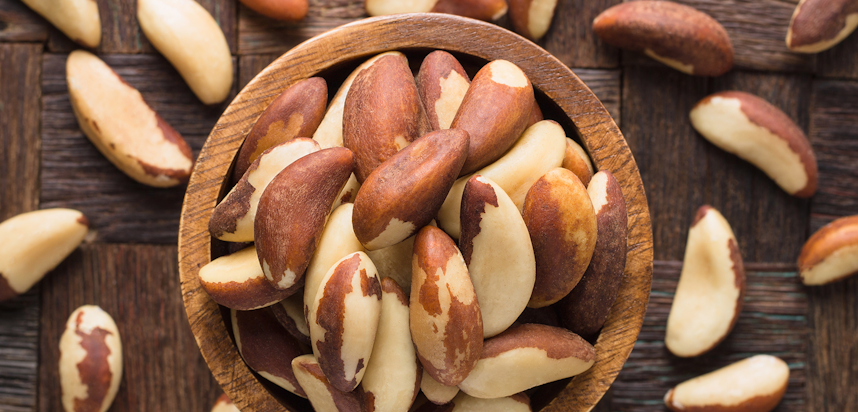

What are Brazil nuts?
Technically not nuts at all, Brazil nuts are the seed of the Brazil nut tree (in the Lecythidaceae family), famously native to the Amazon rainforest. The seeds are contained in the nutshell of the fruit, which can weigh up to 2kg.
Brazil nuts are rich in healthy, monounsaturated fat, vitamin E, and other vitamins and minerals, but they are most famous for the large proportional amount of selenium they contain. Selenium is a powerful antioxidant that aids the health of the immune system. Brazil nuts also contain ellagic acid which adds to the antioxidant properties, as well as being anti-inflammatory. Occasionally they are ground down into flour and used for cooking and baking.
Brazil nuts can be found in
Chocolates and other confectionery, cakes, Muesli, Christmas fruit and nut mix. Brazil nuts are frequently eaten on their own as a healthy snack, and used to decorate cakes and other baked goods.
Potential cross-reactivity with
To some extent Cashews and to a lesser extent Almonds and Pistachios
Can you be allergic to one kind of Tree Nut and not another?
Yes you can be allergic to one kind of Tree Nut but be able to safely eat other varieties. Different types of Tree Nuts contain different proteins, and it is the individual proteins that can trigger an allergic reaction.
However, some Tree Nuts are closely related to each other, in which case there may be cross-reactivity.
You may also be interested in…


You may also be interested in…
Solutions Spotlight: Allergen & Nutritional Data Search
ReadCashew nuts
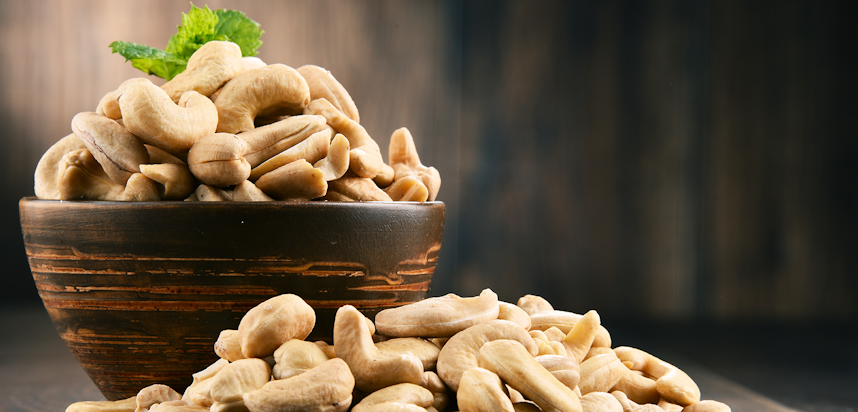

What are Cashew nuts?

Cashew nuts are the seed of the tropical and evergreen Cashew tree, a member of the Anacardiaceae family which grows Cashew apples. Cashews have a lot in common with legumes and people with a Cashew allergy may also be allergic or intolerant to foods such as Peanuts or chickpeas.
Like many other nuts, Cashews are high in protein, healthy fat, vitamins, minerals and fibre. They can be used to help regulate blood sugar and aid weight management and contribute to heart health. They also contain the bone-strengthening mineral magnesium, and copper - which is thought to be good for the brain and the immune system.
When raw, cashews contain the toxic substance urushiol, which is why before being sold they are generally cooked and processed to remove this substance. The Cashew will still have a “raw” look and texture, which is why most people assume they are eating raw Cashews, but genuine raw Cashews are not safe for people to eat.
Cashews are found in
Many Asian dishes (including the popular dish Cashew chicken), satay, stir-fry, sauces, pestos, granola, cereal bars, nut mixes and bar snacks, cookies and other baked goods.
Cashews are also a popular vegan dairy substitute, made into “butter” or “cheese”.
Potential cross-reactivity with
Pistachio and to a lesser extent Almonds and Brazil nuts.
Hazelnuts

What are Hazelnuts?
Hazelnuts, also sometimes known as cobnuts or filberts (depending on the species) are the fruit of the hazel tree (Betulaceae family ), grown in Europe - particularly Italy and Turkey - and America. Hazelnuts are known for their sweet, creamy taste, and are usually sold without their recognisable brown shell.
Hazelnuts are eaten both raw and toasted, and they have a high fat content and are rich in omega-3, which helps with heart health and blood pressure. They also contain antioxidants and cholesterol-reducing, anti-inflammatory phenolic compounds.
Hazelnuts are found in
Nutella, chocolate bars, cereals, muesli, bar snacks, cereal bars, pastries, cakes, biscuits, ice cream, cookies, hot drinks, Frangelico liqueur, brownies, other desserts.
Hazelnut oil is also used for cooking and frying.
Potential cross-reactivity with
To some extent Cashews and Brazil nuts, to a small extent, walnuts and pistachios.
What is the most common Tree Nut allergy?
The most common Tree Nut allergy varies from country to country - in the UK it’s thought to be Hazelnut or Cashew.
Whilst not a Tree Nut, Peanuts are generally considered the most high-profile allergen.
Macadamia nuts

What are Macadamia nuts?
Indigenous to Australia (specifically regions of northeastern New South Wales and central and southeastern Queensland), Macadamia nuts are the fruit of the Macadamia tree, of the flowering plant Proteaceae family. Macadamia nuts were famously commercially produced on a wide scale in nineteenth century Hawaii after the seeds were introduced there, and currently South Africa is the world’s largest Macadamia producer.
Macadamias have a higher fat content then other Tree Nuts, and in addition to these healthy fats they also contain manganese, thiamin, and copper - as well as being rich in protein and fibre. They also contain palmitoleic acid (and are in fact one of the only sources of it) which helps motivate and speed up the metabolism, aiding weight loss. Macadamia nuts are also good for the liver.

Macadamia nuts are found in
Nut mixes, leafy salads, chocolates, cereals, cereal bars, cookies, cakes and other baked goods.
Macadamias are frequently eaten alone, and crushed Macadamia nuts are very popular in Keto and other low-carb diets as a crust or topping for meat and fish.
Potential cross-reactivity with
To a small extent Coconuts and Peanuts.
Pecan nuts
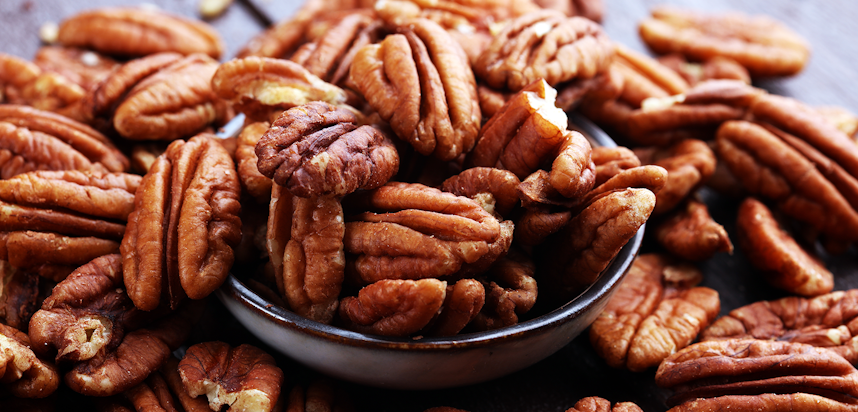

What are Pecan nuts?
Pecan nuts come from the Hickory tree species of Pecan, part of the Juglandaceae family, and particularly associated with the United States of America, where it is native in several of the southern states (as well as parts of northern Mexico) and even appears as part of the state symbols of Alabama, Arkansas, California, Oklahoma and Texas.
With a glossy shell, at first glance it might be surprising that the Pecan is related to the Walnut but they share a bumpy surface on the nut itself.
Pecans are rich in flavour - they are the fattiest of all nuts, and contain high amounts of monounsaturated fat. This means they can help lower cholesterol. They are also rich in antioxidants and vitamins and minerals, and have a high protein content which makes them a good choice for vegans and vegetarians who don’t get protein from meat.
d plant protein, they're chock-full of good fat, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Pecans are found in
Pecan pie, pancakes, muffins, pastries, sweet pies, cookies, cakes, tarts and other baked goods, confectionery, chocolates and chocolate bars. They are also sometimes used in savoury dishes such as salads.
Potential cross-reactivity with
Walnuts.
Can you differentiate between the different types of Tree Nut on Erudus?
Yes, you can specify which Tree Nut sub-category your product does or does not contain when entering product specifications on Erudus.
You can select “Nuts (And products there of)” and then also select from the following to specify which exact nut(s) are among the ingredients.
Almond nuts, Hazelnuts, Walnuts, Cashew nuts, Pecan nuts, Brazil nuts, Pistachio nuts, Macadamia nuts and Queensland nuts.
Pistachio nuts
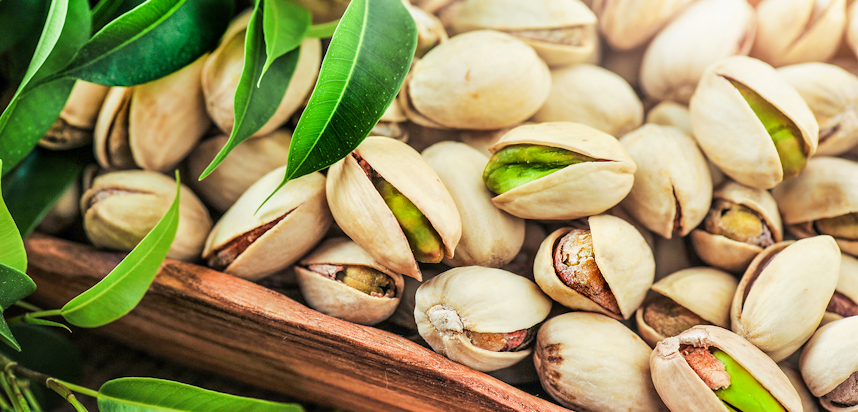

What are Pistachio nuts?
Pistachio nuts come from the small Pistachio tree, of the Anacardiaceae family, native to Central Asia and the Middle East (particularly modern Afghanistan and Iran). Pistachio nuts are actually the seeds of the tree,and are distinctive for their green colour, which is caused by the pigment chlorophyll - also found in other green fruits and vegetables.
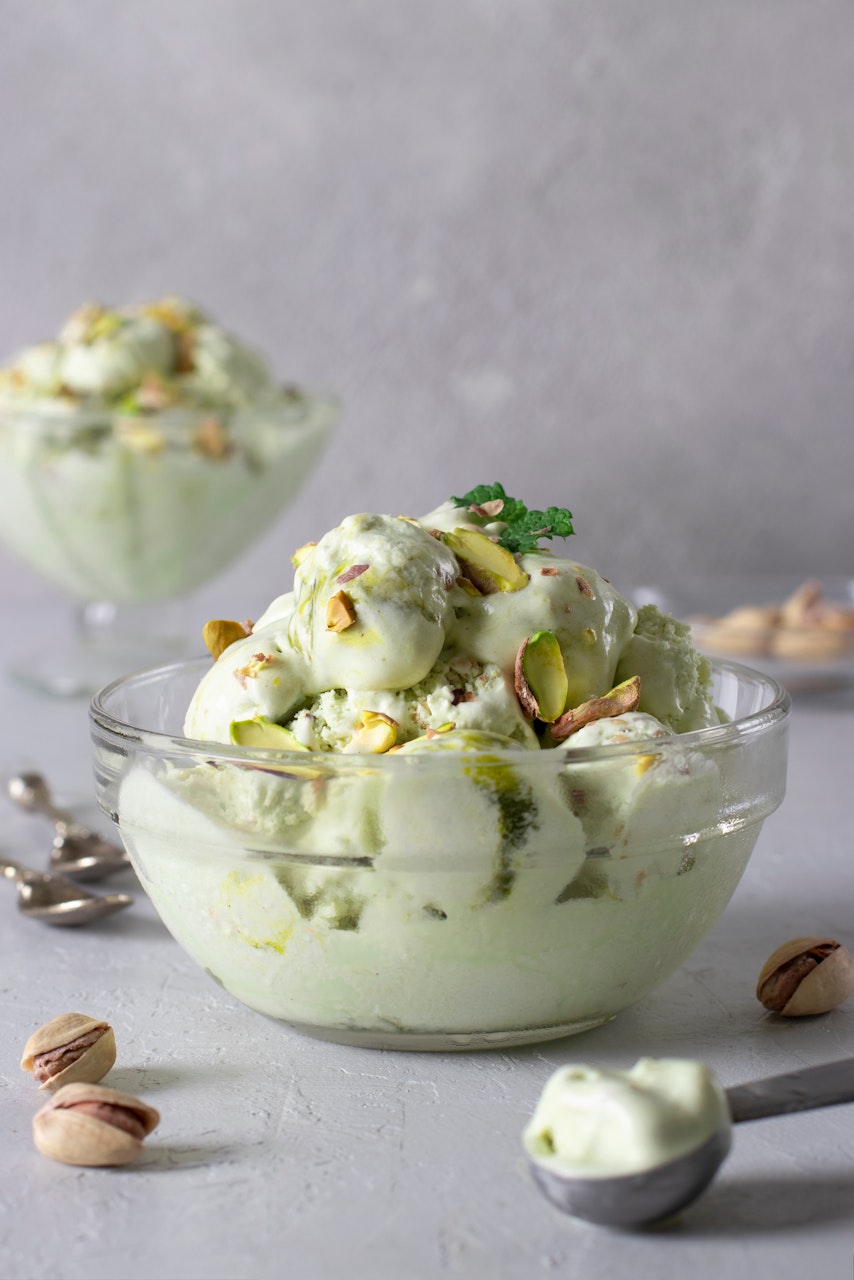

Often sold in their shell, which can also be used for plant mulch, Pistachio nuts can help with sleep, due to the high magnesium and B6 content, and can also aid constipation due to the fibre in them. They also contain good levels of unsaturated fat, potassium, and other vitamins and minerals.
Pistachios are found in
Salads, Pilaf, curry, Indian desserts, Turkish dishes and desserts such as baklava, halvah, ice-cream, natural food colouring, yoghurt, cereal bars. Pistachio nuts are a very popular snack food and are also frequently ground down and put into sauces to add sweetness.
Potential cross-reactivity with
Cashews and to a lesser extent Almonds.
Queensland nuts
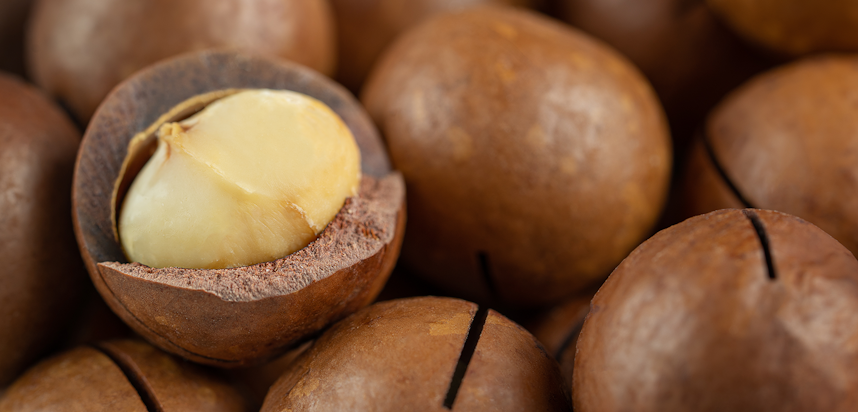

Queensland nuts are the same as Macadamia nuts, also known as bush nut, maroochi nut, bauple nut and Hawaii nut.
The tree is native to Queensland, Australia.
Walnuts
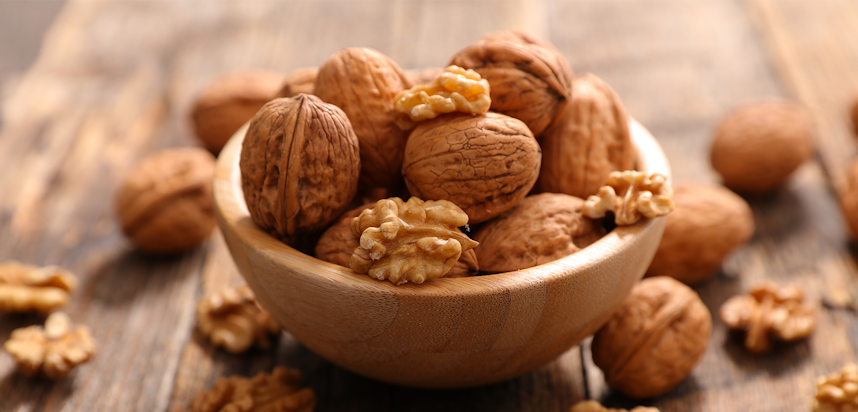

What are Walnuts?
Walnuts are single-seeded stone fruits more commonly referred to as “nuts”. They come from the walnut tree, of the Juglandaceae family and produced in large volumes by China, America, Iran and Turkey.
Walnuts have a hard shell and are fully ripened in Autumn, at which stage the shell will be wrinkled and brown. For consumption the shell is removed, revealing a knobbly golden nut with a mild, earthy flavour.
Walnuts are known for memory-enhancing properties, due to the ellagic acid content, as well as polyunsaturated fats, vitamin E, folate and other vitamins and minerals.
Walnuts are also thought to help the gut, by increasing the amount of probiotic bacteria.
Walnuts are found in
Salads, pizza toppings, yoghurt, ice cream, cakes, cookies, biscuits and other baked goods, Christmas mixes, granola, cereal bars, pesto and other sauces, bread. Walnuts are also frequently eaten alone.
Potential cross-reactivity with
Pecans and to a much lesser extent Brazil nuts, Cashews, Almonds, Hazelnuts and Pistachios.
What are the 14 major food allergens?
Below are the 14 major food allergens. Pre-packed food sold in the UK, and the rest of the European Union, must clearly indicate on the label if it contains any of these foods as an ingredient.
The other major food allergens are






